Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...

Start your journey in data science with Python from scratch. Learn basics, key libraries, real-world applications, and career opportunities in this beginner-friendly 2026 guide.
Python for data science intro is the first step for anyone who wants to enter the world of analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. Python has become the most preferred programming language for data science because of its simplicity, flexibility, and powerful libraries. Whether you are a beginner, a working professional, or a student exploring career opportunities, learning Python can open doors to high-demand roles in data analytics and AI. In this guide, you will understand how Python works in data science, the tools involved, real-world use cases, and how you can start your journey in a practical and career-focused way.
Over the last decade, Python has grown rapidly in the technology ecosystem. It is widely used in analytics, automation, AI development, and research. The reason is simple — Python is easy to learn and powerful to implement.
Unlike other complex programming languages, Python has readable syntax. This means beginners can quickly understand and write code without feeling overwhelmed. For data science, Python offers strong community support and an extensive collection of libraries designed specifically for handling data.
Another reason Python dominates is its integration capability. It works smoothly with cloud platforms, big data tools, and AI frameworks. Companies across industries prefer Python for building scalable data solutions.
If you explore professional programs like data science certification courses, you’ll notice Python is always the foundation of the curriculum.
Data science is the process of collecting, cleaning, analyzing, and interpreting data to make better decisions. It combines programming, statistics, and business understanding.
When businesses analyze customer behavior, predict sales, detect fraud, or recommend products — they use data science techniques.
Python plays a major role in each stage:
Without Python, executing these tasks would require multiple tools. With Python, everything can be handled in one ecosystem.

Python’s real power in data science comes from its libraries. These libraries are pre-written codes that make complex operations easier.
NumPy is used for numerical computations and handling arrays. It allows faster mathematical operations compared to traditional Python lists.
Pandas is one of the most important libraries. It is used for data manipulation and analysis. With Pandas, you can clean datasets, handle missing values, and organize structured data efficiently.
Matplotlib and Seaborn help in data visualization. They allow you to create graphs, bar charts, pie charts, and advanced statistical visualizations.
Scikit-learn is widely used for machine learning algorithms like regression, classification, and clustering.
These tools together form the backbone of Python data science workflows.

A data science project follows a structured approach.
First comes problem understanding. Before writing code, a data scientist must understand what business question needs to be solved.
Next is data collection. Data can come from databases, APIs, Excel files, or online platforms.
After collecting data, cleaning becomes necessary. Real-world data often contains errors, missing values, or duplicates. Python’s Pandas library helps in fixing these issues.
Once the data is clean, exploratory data analysis begins. Here, visualization tools help identify patterns and trends.
Finally, machine learning models are built and evaluated. These models help predict outcomes or classify information.
This entire process becomes efficient when supported by professional training programs such as Python training courses that focus on practical implementation.
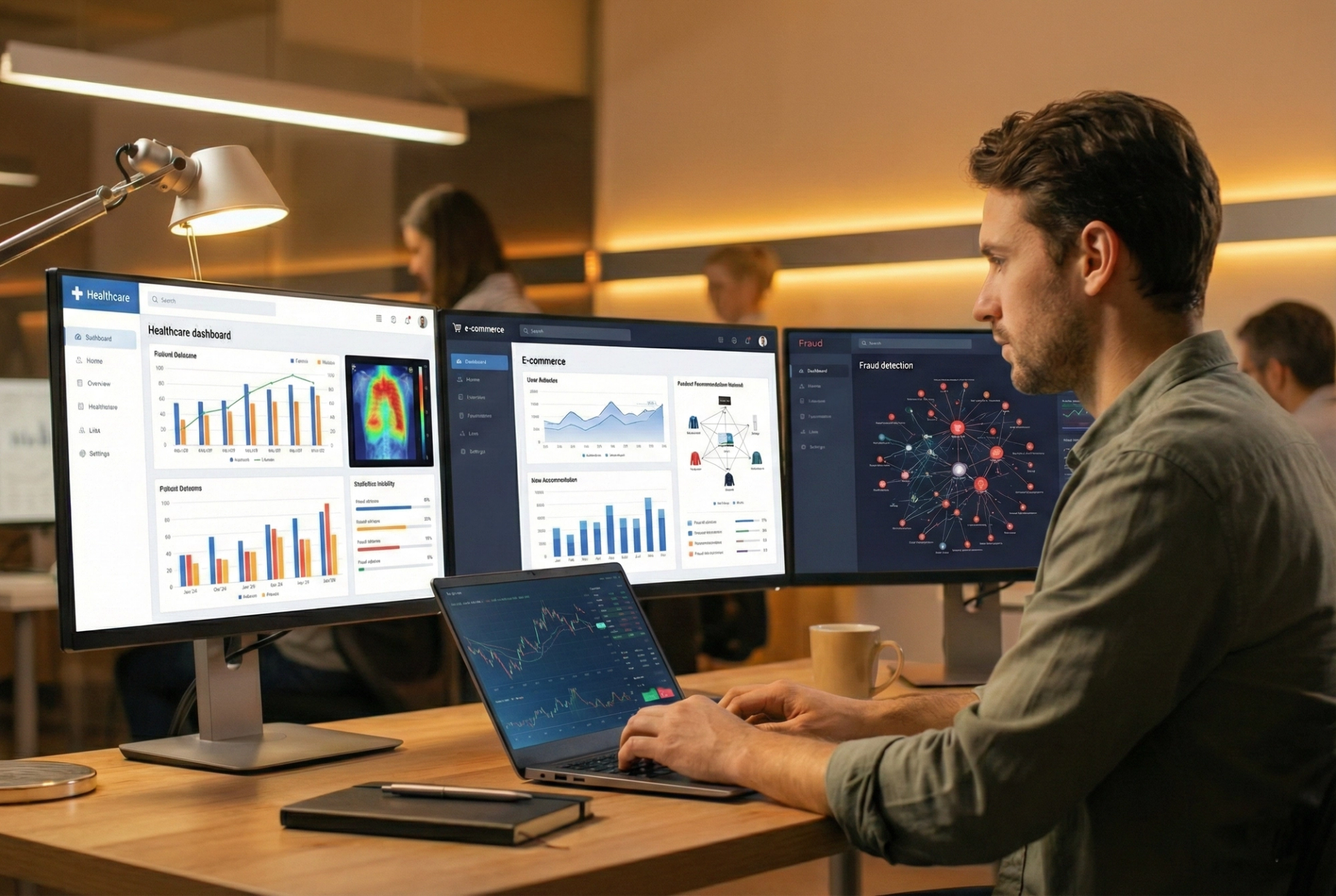
Python is not just theoretical. It is actively used across industries.
In e-commerce, companies use Python to build recommendation systems that suggest products to customers.
In banking, Python helps detect fraudulent transactions through predictive modeling.
In healthcare, it is used to analyze patient data and predict disease risks.
In finance, Python is widely used for stock market prediction and algorithmic trading.
These applications show that data science skills are future-proof and high in demand.
Professionals often enhance their skills with machine learning courses to stay competitive.

Starting with Python does not require a technical background. The first step is understanding basic programming concepts like variables, loops, and functions.
Once comfortable, you can move to libraries like NumPy and Pandas.
Practicing small projects like analyzing sales data or visualizing survey results builds confidence.
Consistency matters more than speed. Many learners combine self-study with structured guidance through online data analytics programs for better career outcomes.
The demand for data professionals is growing rapidly. Roles include:
Companies prefer candidates with hands-on project experience and knowledge of Python tools.
A structured learning path with AI and data science training improves placement opportunities.
Salaries in this domain are competitive, especially for professionals who combine technical knowledge with business understanding.
Many beginners try to jump directly into advanced machine learning without understanding basics. Strong fundamentals in Python and statistics are essential.
Another mistake is ignoring data cleaning. Clean data determines model accuracy.
Also, avoid memorizing code. Instead, understand logic and application.
Building small projects and solving real datasets strengthens problem-solving skills.
Python continues to evolve with advancements in AI, automation, and cloud computing. Integration with big data platforms and AI frameworks ensures its long-term relevance.
Emerging technologies like Agentic AI and autonomous workflows are also built using Python-based ecosystems. This makes learning Python even more valuable for the future.
The combination of automation, AI agents, and data-driven decision-making will define the next decade of digital transformation.
Yes, Python is one of the most widely used languages in data science due to its simplicity and powerful libraries.
With consistent practice, beginners can grasp fundamentals in 3–6 months.
No, many non-technical learners successfully transition into data science with structured learning.
Both are useful, but Python is more versatile and widely adopted in industry.
Yes, demand for data professionals continues to grow globally.
Learning Python for data science is one of the smartest career decisions in today’s digital economy. Python offers simplicity, scalability, and strong industry demand. From data cleaning to machine learning modelling, Python provides a complete ecosystem for solving real-world problems. Whether you aim to become a data analyst, machine learning engineer, or AI specialist, mastering Python builds a strong foundation. With the right guidance, consistent practice, and exposure to real projects, you can confidently step into the rapidly growing field of data science and secure long-term career growth.

Shoeb Shaikh is a seasoned Software Testing and Data Science Expert and a Mentor with over 14 years of experience in the field. Specialist in designing and managing processes, and leading high-performing teams to deliver impactful results.
At CDPL Ed-tech Institute, we provide expert career advice and counselling in AI, ML, Software Testing, Software Development, and more. Apply this checklist to your content strategy and elevate your skills. For personalized guidance, book a session today.