Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...

The End-to-End Data Science Workflow explains how raw data is transformed into intelligent, real-world solutions. From defining business objectives and collecting data to preprocessing, model training, evaluation, and deployment, this guide covers every stage of a complete data science project lifecycle. Whether you are a beginner or an aspiring professional, understanding this structured workflow helps you build scalable, production-ready machine learning models that deliver measurable business value.
Learn the complete End-to-End Data Science Workflow, from data collection and preprocessing to model building, evaluation, and deployment. This practical guide explains each stage in simple terms to help you build real-world, production-ready machine learning projects.
The End-to-End Data Science Workflow is the structured process that transforms raw data into actionable business intelligence through analysis, modeling, and deployment. In today’s digital economy, organizations rely heavily on data-driven decisions, making it essential to understand how a data science project moves from initial data collection to full-scale model deployment. Whether you are a beginner exploring data science courses or a professional looking to strengthen your practical knowledge, mastering the complete workflow ensures clarity, efficiency, and scalability in real-world projects. This guide explains each stage in simple, practical language so that anyone interested in data science can understand how modern AI systems are built and deployed.
Understanding the Foundation of Data Science Projects
Every successful data science initiative begins with clarity. Before collecting data or writing code, it is essential to understand the business objective. Organizations do not build models for experimentation alone; they aim to solve problems such as predicting customer churn, detecting fraud, improving recommendation systems, or optimizing supply chains.
A strong foundation includes defining measurable goals, identifying constraints, and determining success criteria. This phase is often underestimated, but without a clearly defined problem statement, even the most advanced algorithms cannot deliver value. In real-world scenarios, data scientists collaborate with stakeholders to translate business questions into analytical tasks.
The workflow then moves toward identifying relevant data sources. These may include internal databases, APIs, IoT sensors, cloud storage systems, or third-party datasets. Understanding where the data originates ensures better reliability and governance throughout the project lifecycle.
Data Collection and Data Understanding
Data collection is the backbone of any machine learning pipeline. Without high-quality data, model accuracy becomes unreliable. Data can be structured, such as spreadsheets and relational databases, or unstructured, such as images, text documents, and audio files.
Once collected, the next crucial stage is data understanding. This involves exploratory data analysis where patterns, anomalies, and relationships are examined. Statistical summaries, visualizations, and correlation analysis help identify trends and inconsistencies. At this stage, professionals often discover missing values, outliers, or biased distributions that may influence the model's performance.
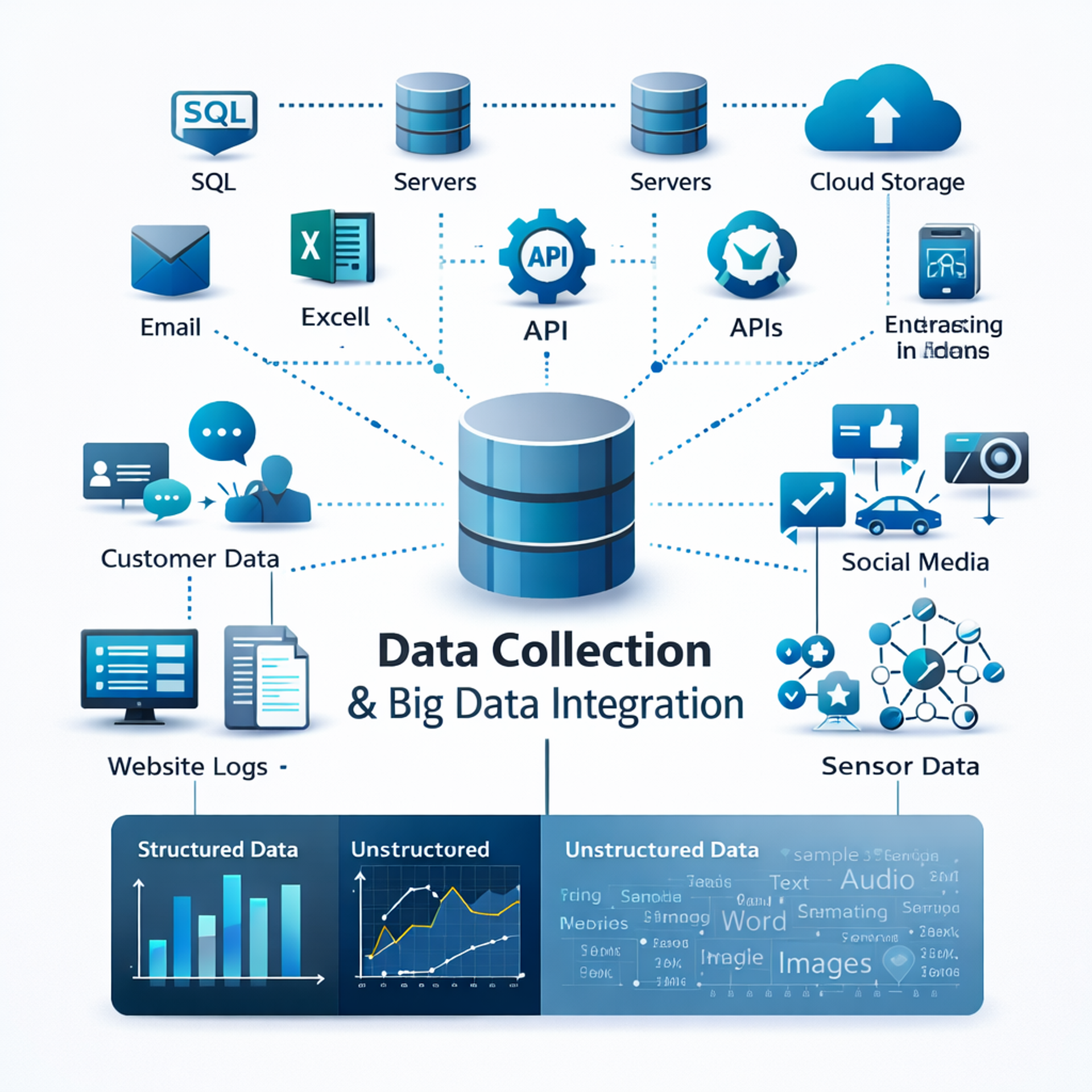
Modern data science workflows emphasize data governance and ethical handling. Ensuring compliance with privacy regulations and maintaining data integrity protects organizations from legal and operational risks. Strong fundamentals taught in a professional data analytics course improve analytical thinking.
Data Cleaning and Pre-processing
Raw data is rarely ready for modeling. It often contains inconsistencies, duplicate entries, missing values, and irrelevant attributes. Data cleaning transforms chaotic datasets into reliable analytical inputs.
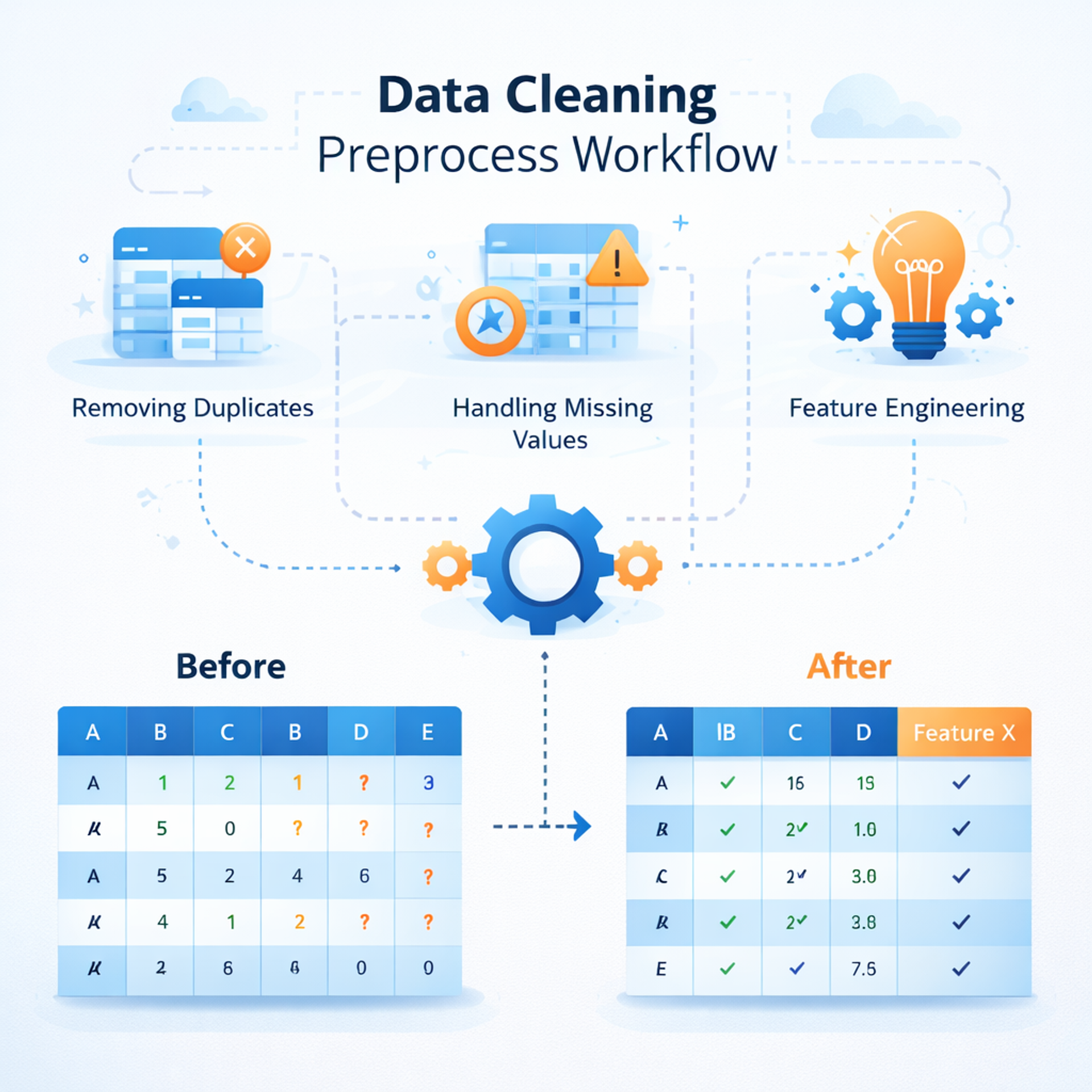
Preprocessing involves handling null values, normalizing numerical features, encoding categorical variables, and scaling data. In addition, feature engineering plays a significant role in improving model performance. By creating meaningful derived variables, data scientists enhance predictive power without increasing complexity.
This stage directly impacts accuracy. A well-preprocessed dataset can significantly outperform a complex model trained on poor-quality data. Many industry experts emphasize that nearly seventy percent of project time is spent in this phase, reflecting its importance in the end-to-end data science workflow.
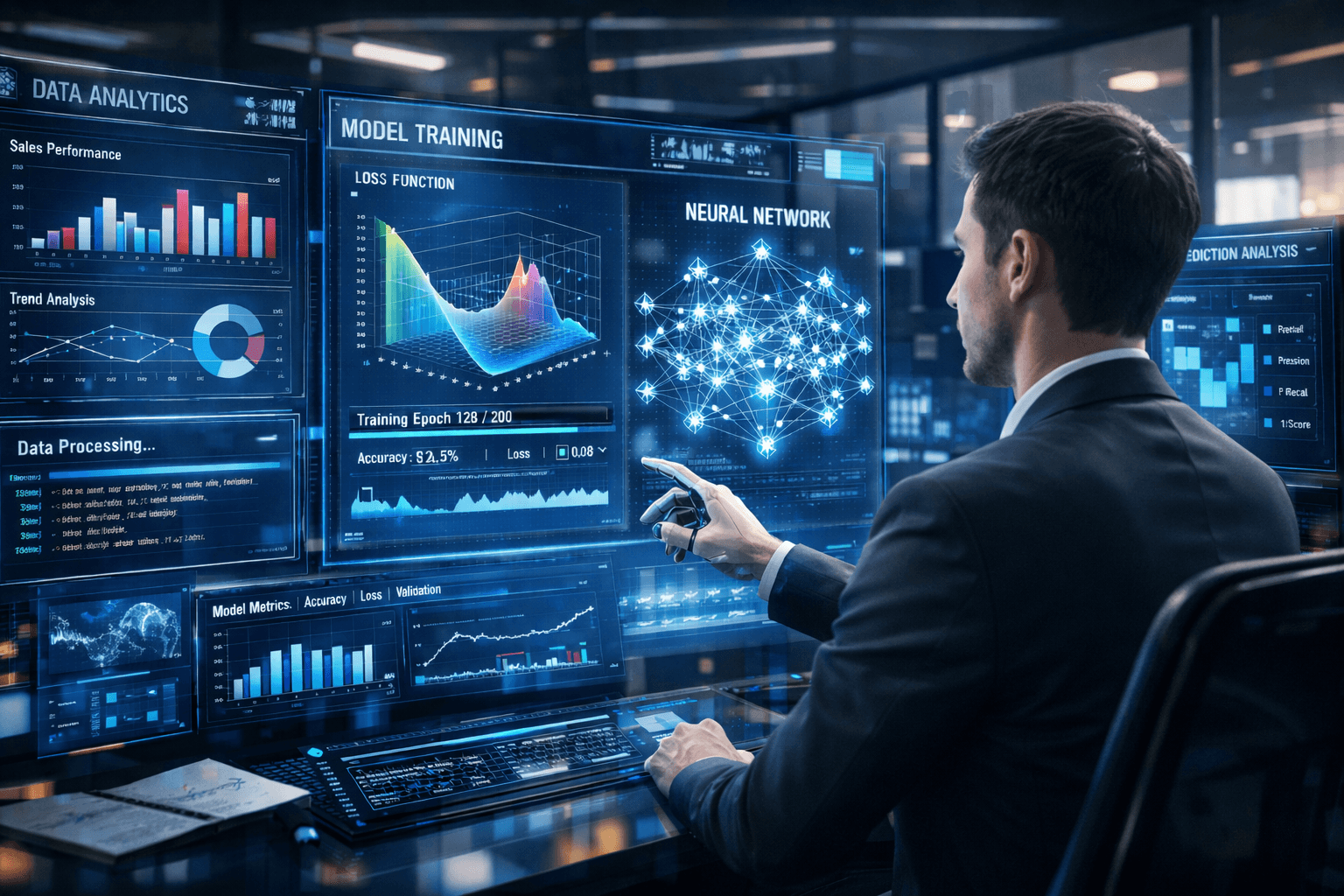
Model Selection and Development
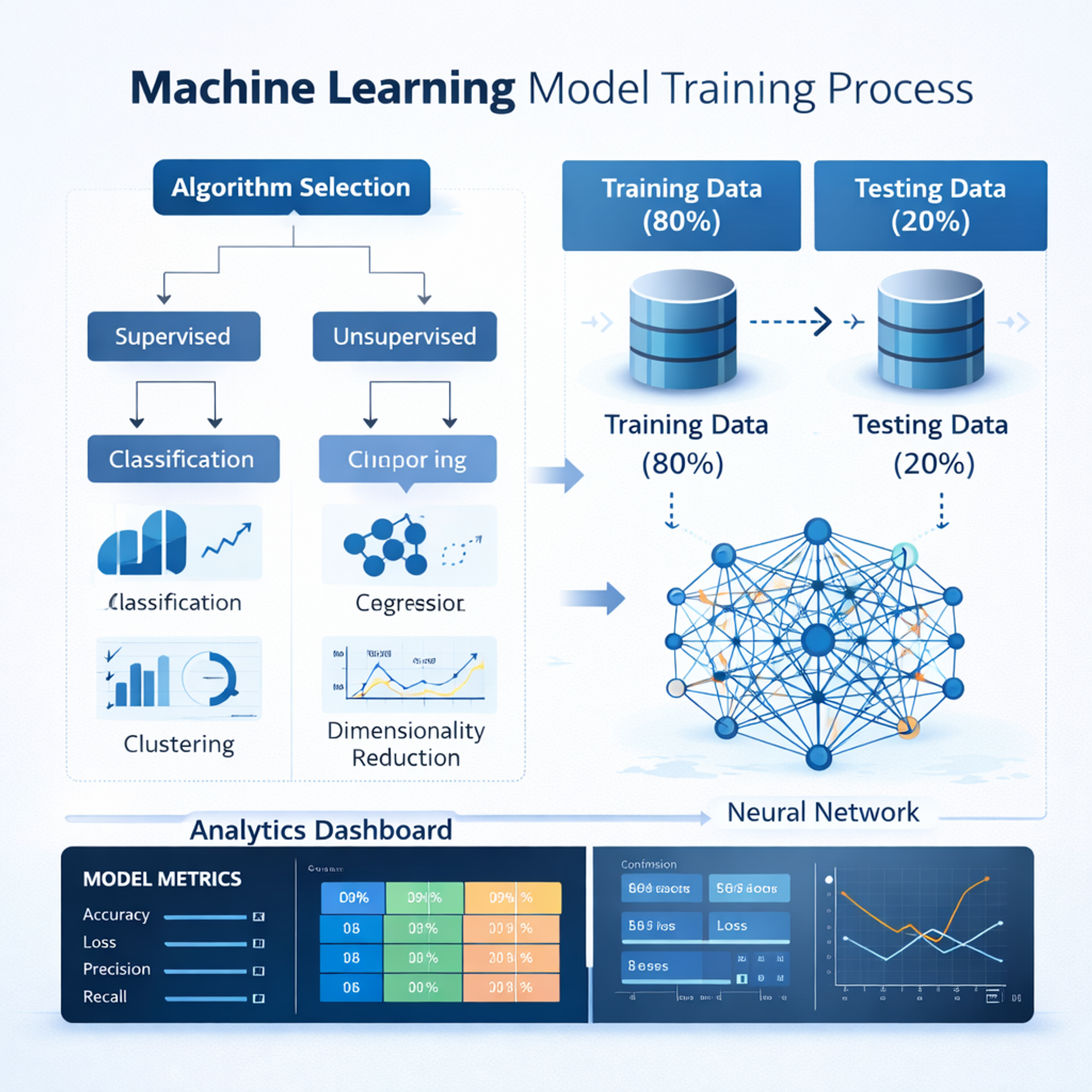
After preparing the dataset, the next phase is model selection. The choice depends on the problem type. Classification problems may use logistic regression, decision trees, or neural networks, while regression tasks rely on linear regression or ensemble techniques.
Model development involves splitting the dataset into training and testing subsets. The training data helps the algorithm learn patterns, while testing data evaluates generalization performance. Cross-validation techniques ensure robustness by reducing overfitting.
Hyperparameter tuning refines the algorithm further. Adjusting learning rates, tree depth, or regularization parameters improves predictive performance. During this stage, experimentation is common, but it remains guided by structured evaluation metrics.
Evaluation metrics vary depending on the objective. Accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and ROC-AUC are common for classification tasks. For regression problems, metrics such as mean absolute error and root mean squared error provide insights into prediction quality.
Model Evaluation and Validation
Evaluation ensures that the model performs well beyond the training dataset. A strong validation strategy prevents overfitting, where a model memorizes patterns instead of learning generalizable relationships.
In real-world data science projects, confusion matrices and performance curves help interpret strengths and weaknesses. If a model performs poorly, iteration is required. This may involve revisiting feature engineering, adjusting hyperparameters, or even selecting a different algorithm.
Beyond technical accuracy, interpretability has become essential. Businesses require transparency to trust AI-driven systems. Techniques such as feature importance analysis and model explainability tools enhance accountability and confidence.
Model Deployment and Integration
Deployment transforms a trained model into a functional system accessible to users. This stage bridges the gap between experimentation and real-world application. Deployment may occur through web APIs, cloud platforms, or embedded systems.
Modern workflows incorporate MLOps, which ensures continuous integration, monitoring, and retraining. Models degrade over time as data patterns change, a phenomenon known as data drift. Monitoring systems detect performance decline and trigger retraining when necessary.
Scalability is another consideration. As user demand grows, infrastructure must handle increasing traffic without compromising speed. Cloud-native solutions provide flexibility and reliability.
Integration with business systems ensures that predictions translate into actionable insights. For example, a churn prediction model may integrate with CRM software to automate retention campaigns.
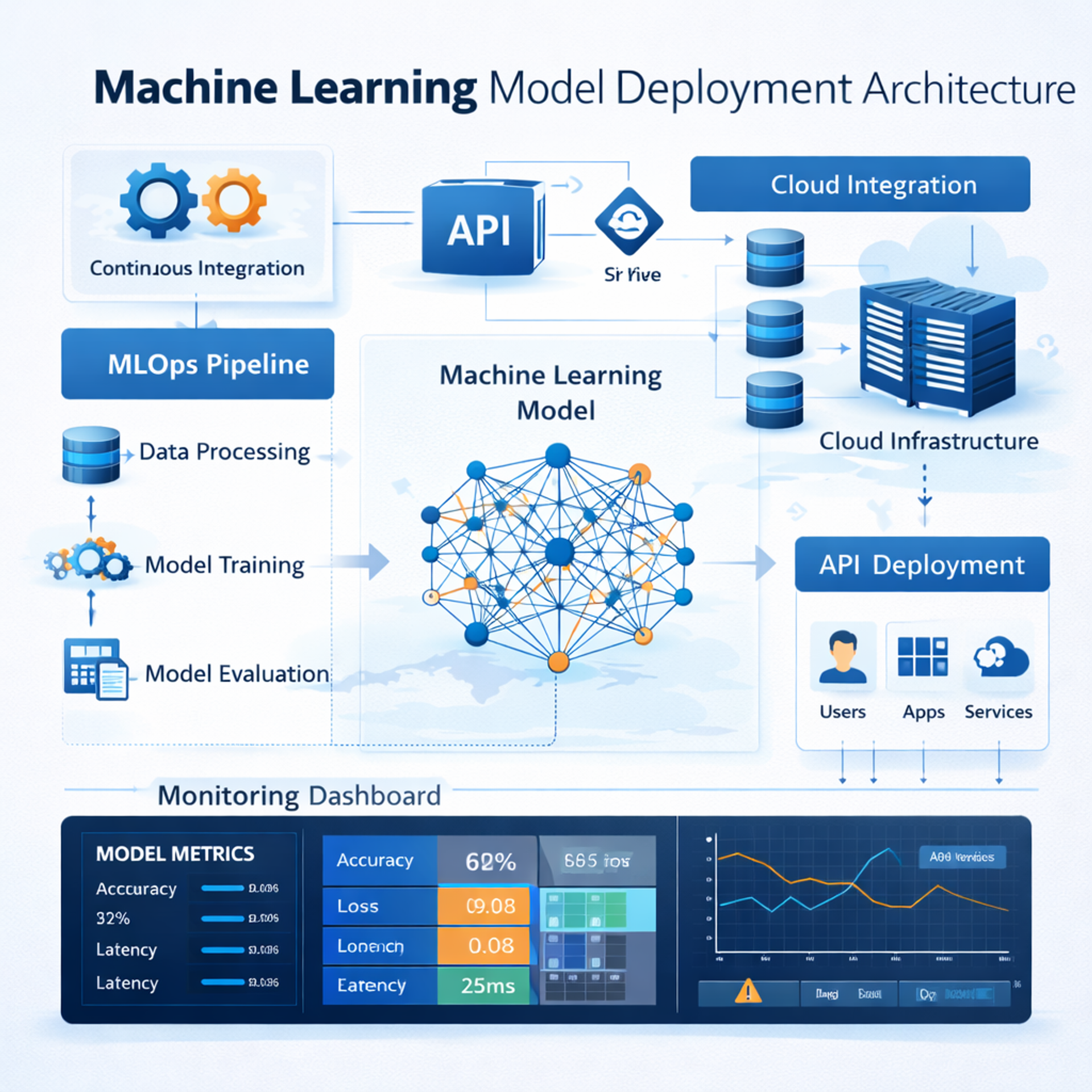
Monitoring, Maintenance, and Continuous Improvement
The data science lifecycle does not end after deployment. Ongoing monitoring ensures consistent performance. Metrics such as latency, prediction accuracy, and system stability must be tracked continuously.
Feedback loops play a crucial role in improving models. By analyzing new incoming data, organizations refine their systems to maintain competitiveness. Continuous improvement reflects the evolving nature of artificial intelligence in business environments.
Real-World Application of the End-to-End Workflow
Understanding the workflow theoretically is valuable, but practical application solidifies knowledge. In industries such as healthcare, finance, e-commerce, and education, data science drives innovation.
A recommendation system in an online learning platform, for instance, follows the complete lifecycle. It collects user interaction data, cleans and preprocesses information, trains collaborative filtering algorithms, evaluates performance, and deploys predictions to enhance user engagement.
Professionals who master this structured approach gain confidence in managing large-scale projects. This is why comprehensive training programs emphasize project-based learning rather than isolated theoretical modules.
Why Learning the Complete Workflow Matters
Structured AI & Data Science certification programs help learners master real-world workflows. Many beginners focus only on coding algorithms. However, real success in data science depends on understanding the entire pipeline. The ability to move seamlessly from data collection to deployment differentiates skilled practitioners from hobbyists.
Organizations prefer professionals who understand business alignment, data engineering fundamentals, modeling strategies, and deployment mechanisms. A holistic perspective increases employability and career growth opportunities.
Training in the full workflow also builds strategic thinking. Instead of experimenting randomly, practitioners learn structured problem-solving methods aligned with measurable outcomes.
FAQ Section
What is an End-to-End Data Science Workflow?
It is the complete lifecycle of a data science project, starting from defining the business problem and collecting data to building, evaluating, and deploying a predictive model.
Why is data preprocessing important?
Preprocessing ensures data quality and consistency, directly influencing model accuracy and reliability.
What is MLOps in model deployment?
MLOps combines machine learning with DevOps principles to automate deployment, monitoring, and maintenance of models in production.
How long does a typical data science project take?
The duration varies depending on complexity, data availability, and business requirements, but most time is spent in data preparation and validation.
Can beginners learn the complete workflow?
Yes, structured courses and guided projects help beginners understand the process step by step.
Conclusion
The End-to-End Data Science Workflow represents more than a technical process; it is a strategic framework for transforming raw information into meaningful solutions. From defining objectives and collecting data to deploying scalable models, each stage contributes to delivering measurable business value. Understanding this lifecycle equips aspiring professionals with practical insight and prepares organizations to harness the true potential of artificial intelligence. By mastering this structured approach, individuals not only improve their technical proficiency but also gain the confidence to build reliable, impactful, and future-ready data-driven systems.

Cezzane Khan is a dedicated and innovative Data Science Trainer committed to empowering individuals and organizations.
At CDPL Ed-tech Institute, we provide expert career advice and counselling in AI, ML, Software Testing, Software Development, and more. Apply this checklist to your content strategy and elevate your skills. For personalized guidance, book a session today.